This CMS design tool helps you get the most from the HubSpot COS.
.jpg?width=630&height=328&name=Media%20(14).jpg)
1. Basic simulators with 3D visualization
Basic, entry-level G-code simulators exist to help beginners and trainees learn the ropes by loading and running G-code in a stripped-back environment.
Tools like NC Viewer and CAMotics are useful tools for checking simple G-code, 3D toolpaths, or 2D line plots.
Pros: Low-cost, easy-to-use, and often capable of running through a browser. Simple and comfortable entry into G-code programming, including spotting syntax errors or odd movements.
Cons: Not suitable for serious manufacturing of precision parts and components by experienced engineers. These tools generally offer little to no collision detection, kinematics, or controller logic, making them useful for a sanity check or for education.
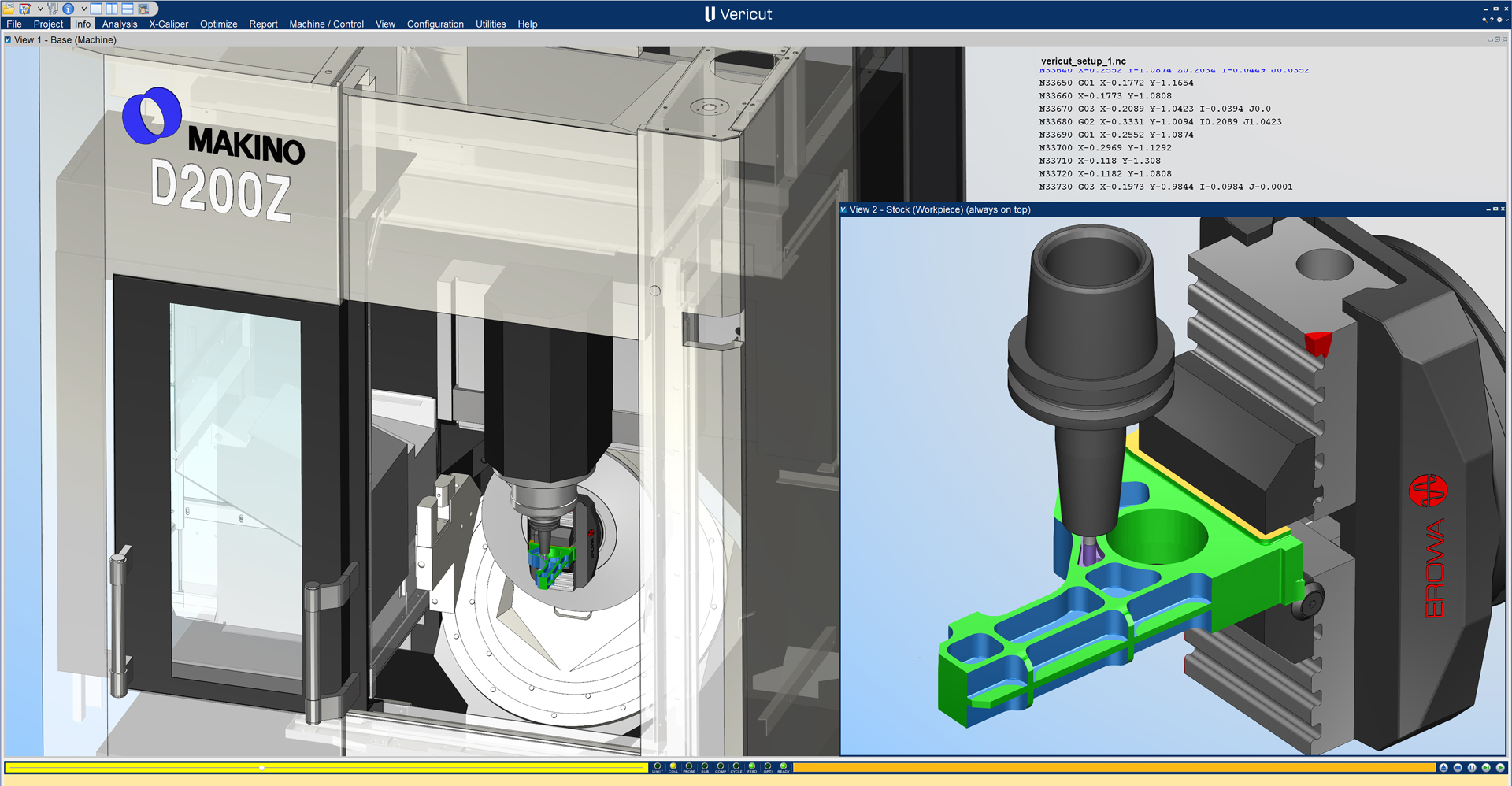
2. Full machine and G-code simulation systems
Full machine simulation systems, like Vericut CNC Simulation Software, create highly detailed and realistic digital twins of a CNC machine, including its axes, spindle(s), tooling, etc.
They replicate real-world G-code and machine behavior supporting the complex cutting operations needed to produce high-precision parts, like 5-axis machining, mill-turn, and multi-spindle setups.
Vericut is the leading example of full machine simulations, trusted by the biggest and the best in top industries. Take a look at our case studies today.
Learn how Vericut Verification helped Sandvik-Gimo achieve a 15.3% energy saving per workpiece
This G-code simulation software is critical for validating programs on expensive machines producing critical components. Unlike basic simulators, products like Vericut can simulate machine limits, controller behavior, and multi-channel code, while also providing a detailed 3D visualization of the machine and parts.
The result? Your engineers and machinists can quickly and easily detect issues that could lead to overtravel, collisions, and inefficiencies.
.jpg?width=630&height=356&name=Media%20(15).jpg)
3. CAM-integrated simulators
Some simulators are built directly into popular CAM packages. This integration is popular choice for its simplicity and fast checks, but it's crucial to note that CAM-integrated simulators do not verify or simulate the actual G-code.
.jpg?width=630&height=317&name=Media%20(16).jpg)
1. NC Code interpretation and processing
This is the accurate processing of G-code and logic as a real CNC control would. Vericut excels in this regard by replicating every facet of real-world CNC behaviour.
Proper NC code processing ensures that what you see in simulation is a true representation of what will happen on your machine, which is crucial for trust in the simulation results. It’s not just about moves; it’s also about respecting travel limits, feedrate overrides, tooling data, and so on.
2. Toolpath verification & optimization
One of the biggest benefits of G-code simulators is seeing a visual depiction of your toolpath. Good simulators provide a graphical toolpath trace that lets you see where your cutter will travel.
You can then look through each step of the code to see what rapid movements look like, where toolpaths won’t complete features, or where an error will occur.
With this feature, machinists and engineers can see exactly how a part will be machined, step-by-step, before any real cutting occurs. Tools like Vericut also offer analysis, making your toolpaths as transparent and simple as possible.
Learn how Vericut Force™ helps AML reduce cycle times by up to 40%
3. 3D model rendering
Modern G-code simulators offer realistic 3D renderings of machine tools, fixtures, and stock. With tools like Vericut, users can rotate, zoom, and analyze the cutting process from any angle and at a speed that suits them.
A strong 3D engine allows the simulator to depict the stock being cut away, the tool model (with correct geometry), holders, fixtures, and even the machine components (table, spindle head, etc.) in motion. For example, Vericut’s simulation creates an exact machining environment in 3D.
4. Virtual material removal
G-code simulators eliminate the need for trial cutting or wasted raw stock by simulating material removal from stock to completed part. The software starts with a defined stock (block, bar, casting, etc.) and subtracts material when the cutter intersects the stock as each motion is executed.
This is crucial for verifying that the final machined part matches the intended design and for finding any machining errors like gouges or excess material left (perhaps due to a missed toolpath).
5. Machine collision detection
G-code simulators simulate interactions between all machine elements: tools, holders, machine heads, spindles, tables, and fixtures. They flag over-travel, axis interference, or improper approach angles in advance to avoid damage.
Advanced simulators continuously monitor for collisions between all entities: tool with part, tool with machine, machine with part/fixture, etc. They also check for scenarios like the tool going beyond machine travel limits or moving too fast into material. Collision detection is arguably the most important feature for preventing damage.
.jpg?width=630&height=361&name=Media%20(17).jpg)
Step 1: Analysis of cost benefits and ROI
If you manufacture simple components in extremely limited quantities, a full-blown machine simulation tool might not make commercial sense.
However, if you’re a large manufacturer of precision parts, ROI for a tool like Vericut is usually achieved after preventing a single crash or scrapped product.
You’ll need to analyse your own financial situation to see what type of G-code simulator suits you best.
Step 2: Consider compatibility
While Vericut works with almost any major machine tool, CAD/CAM software, and tool management system. These interfaces ensure seamless operation with your current tech.
It’s certainly worth speaking with an expert to discover if your CAM system is compatible with your chosen software, if you’ll need plugins, and if your computer systems have the CPU and GPU power to run a G-code simulator.
Step 3: Ease of use
Powerful advanced systems like Vericut may require proper training to use correctly and get the best results. Simpler tools offer guided processes, but lack the depth or flexibility of full G-code simulators.
Vericut offers popular and comprehensive training modules.
Step 4: Support and updates
Choose a G-code simulator that you’re sure is supported for the years to come. This is essential for long-term viability.
Active development and responsive support mean your investment will last years, and any new custom setups you need help with can be dealt with.
Plus, premium partners like Vericut will be more than just software providers; they can act as extensions of your internal engineering team to diagnose and solve manufacturing challenges.
.jpg?width=630&height=358&name=Media%20(18).jpg)
G-code simulation tools will increasingly move to the cloud to move the bulk of the simulation away from local machines. This move improves customers’ ability to access the software at a time or place that suits them.
Advanced machine learning and AI will continue to improve G-code simulators by enhancing pattern recognition and problem-solving abilities. AI, in particular, will allow simulation software to become increasingly conversational and user-friendly for beginners.
.png?width=465&height=311&name=Media%20(1).png)